Billing and eClaims Management
The Billing and eClaims Management domain within the Kenya National Health Terminology Services (KNHTS) encompasses various subdomains critical for the efficient processing, adjudication, and management of healthcare claims. These subdomains ensure that billing and claims operations are standardized, transparent, and compliant with national regulations.
It is categorized in the following subdomains
1. Adjudication:
- Definition: The process of reviewing and deciding on the validity and amount of claims submitted for reimbursement.
- Components:
- Adjudication Rules: Guidelines and criteria used to evaluate claims.
- Review Processes: Steps involved in verifying claim details and determining payment.
- Purpose: Ensures claims are processed fairly and in accordance with payer policies and regulations.
2. Claim Payment Type:
- Definition: Categories of payment methods used to settle claims.
- Components:
- Payment Methods: Different forms of payment such as direct bank transfers, electronic payments, or checks.
- Payment Types: Designations like full payment, partial payment, or co-payments.
- Purpose: Facilitates the management of various payment methods and ensures accurate processing of claim payments.
3. Adjudication Reason:
- Definition: Codes or descriptions explaining why a claim was accepted or denied during the adjudication process.
- Components:
- Reason Codes: Standardized codes for common adjudication reasons.
- Descriptions: Detailed explanations for the adjudication decisions.
- Purpose: Provides transparency and clarity regarding claim decisions, helping providers understand the reasons for payment or denial.
4. Adjustment Reason:
- Definition: Reasons for modifying or adjusting the amount of a claim after initial adjudication.
- Components:
- Adjustment Codes: Codes representing various reasons for adjustments.
- Adjustment Types: Types of changes such as corrections, additional charges, or discounts.
- Purpose: Allows for corrections and adjustments to claims, ensuring accurate billing and payment.
5. Patient Disposition:
- Definition: The status or outcome of a patient's visit or treatment related to claims processing.
- Components:
- Disposition Codes: Codes indicating the outcome of the visit, such as discharged, admitted, or referred.
- Status Descriptions: Descriptions of patient outcomes and their implications for billing.
- Purpose: Helps in categorizing patient outcomes and understanding their impact on claims and billing.
6. Benefits PHC/SHIF:
- Definition: Coverage details for Primary Health Care (PHC) and Social Health Insurance Funds (SHIF).
- Components:
- Benefit Codes: Codes for different types of coverage and benefits under PHC and SHIF.
- Coverage Details: Information on what services are covered under each benefit plan.
- Purpose: Clarifies the benefits available to patients and how they affect billing and claims.
7. Accommodation Type:
- Definition: The type of accommodation provided during a patient’s stay that impacts billing.
- Components:
- Accommodation Codes: Codes for different types of accommodations, such as ward classes or private rooms.
- Type Descriptions: Detailed descriptions of accommodation types and their billing implications.
- Purpose: Ensures accurate billing based on the type of accommodation provided.
8. Claim Status:
- Definition: The current state of a claim within the billing and adjudication process.
- Components:
- Status Codes: Codes representing various stages of a claim, such as submitted, under review, approved, or denied.
- Status Descriptions: Detailed explanations of claim statuses.
- Purpose: Provides visibility into the progress of claims and helps track their lifecycle.
9. Claim Type:
- Definition: Categories of claims based on the nature of the services provided.
- Components:
- Claim Categories: Types such as inpatient, outpatient, or emergency claims.
- Type Descriptions: Detailed descriptions of each claim type.
- Purpose: Facilitates classification and processing of different claim types according to their characteristics.
10. Claim Decision:
- Definition: The outcome of the adjudication process, indicating whether a claim is approved or denied.
- Components:
- Decision Codes: Codes for various claim decisions such as approved, denied, or pending.
- Decision Descriptions: Explanations of the reasons behind each decision.
- Purpose: Provides a clear outcome of the adjudication process and informs further actions.
11. Claim Decision Reason:
- Definition: The rationale provided for the decision made on a claim.
- Components:
- Reason Codes: Codes explaining the decision made, such as policy exclusions or insufficient information.
- Reason Descriptions: Detailed explanations of the reasons for claim decisions.
- Purpose: Enhances transparency by explaining why a particular claim decision was made.
12. Visit Type:
- Definition: The type of healthcare visit or encounter that affects billing and claims.
- Components:
- Visit Codes: Codes for different types of visits, such as consultation, follow-up, or emergency.
- Visit Descriptions: Detailed descriptions of visit types and their billing implications.
- Purpose: Ensures accurate billing based on the type of visit and related services.
13. Waiver:
- Definition: The process or policy by which certain charges or fees are waived or reduced.
- Components:
- Waiver Codes: Codes for different types of waivers, such as financial hardship or policy exceptions.
- Waiver Policies: Guidelines and criteria for granting waivers.
- Purpose: Allows for adjustments to billing based on specific circumstances or policies.
14. Bank:
- Definition: Financial institutions involved in processing payments related to claims.
- Components:
- Bank Codes: Codes representing different banks used for claim payments.
- Bank Details: Information on how payments are processed through various banks.
- Purpose: Facilitates accurate payment processing and tracking through designated banks.
15. Payor:
- Definition: Entities responsible for paying claims, including insurance companies and government bodies.
- Components:
- Payor Codes: Codes for different payors such as private insurers, national health schemes, or government programs.
- Payor Details: Information on the payors' roles and responsibilities in the claims process.
- Purpose: Identifies and manages the entities responsible for reimbursing claims.
16. Momo Networks:
- Definition: Mobile money networks used for processing payments and transactions related to claims Safaricom, Telkom, Airtel etc
- Components:
- Network Codes: Codes for different mobile money providers.
- Transaction Details: Information on how mobile money transactions are processed for claims.
- Purpose: Facilitates payment processing through mobile money platforms, enhancing accessibility and convenience.
17. Payment Modes:
- Definition: Various methods and systems used for processing payments related to billing and claims.
- Components:
- Electronic Payments: Methods such as bank transfers, credit card payments, and mobile money transactions (e.g., M-Pesa).
- Manual Payments: Traditional methods like checks and cash payments.
- Payment Gateways: Systems that facilitate electronic payments and integrate with billing systems.
- Purpose: Provides flexibility and convenience in payment processing, ensuring timely and secure transactions.
These concepts are obtained from Logistics & Supply Chain - LSC
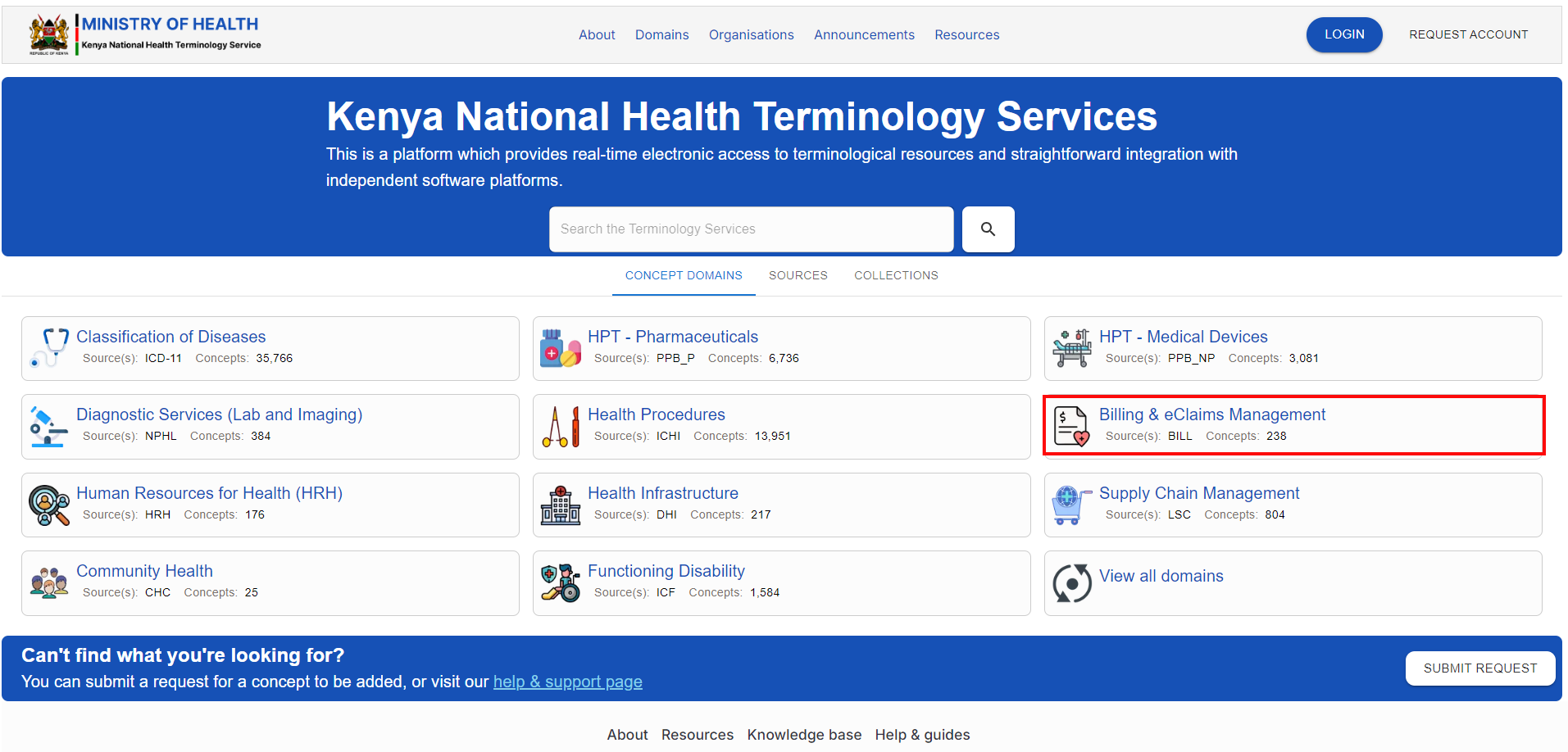
To access the domain, navigate to the KNHTS Homepage Homepage and select the highlighted domain below
Refer to the Classification of Diseases page in this user guide to see navigate around and perform actions related to concepts